ChatGPT Edu | AI Competency Centre
ChatGPT Edu
Table of contents:
ChatGPT Edu is Oxford's enterprise version of OpenAI's leading AI model, designed for sophisticated reasoning, content creation, and analysis.
What ChatGPT Edu Does Best
- Advanced reasoning and analysis - Handles complex problem-solving tasks
- Document drafting and editing - Creates professional content from scratch
- Code writing and debugging - Supports multiple programming languages
- Live web browsing - Incorporates current information into responses
- Text summarisation - Processes lengthy, complex documents
When logging in with an SSO, all current staff and students will join the University of Oxford ChatGPT Edu workspace. The features available in the University of Oxford workspace will be subject to internal governance based on business need and may not be the same as those in consumer versions.
Why you should use ChatGPT Edu
- Saving money. ChatGPT Edu accounts are being made available free at point of use, across the University and colleges, as part of an inclusive offer
- Better security. You can access ChatGPT Edu via your SSO, which gives you more security and convenience than either the Plus or Teams licence.
- Share your GPTs and chats privately with others in the Oxford workspace or with the whole Oxford workspace all at once. We have created an Oxford GPT Library to showcase some of the custom GPTs created and shared within the University's workspace.
- Enhanced data protection: Unlike the free and Plus versions (where you have to manually opt out of allowing your data to be used to train OpenAI’s data models), data you input into ChatGPT Edu is not shared to train OpenAI's models by default. This means you maintain full ownership of all your inputs and outputs, which is important when working with research data or sensitive university information.
- Security assessment. Of all OpenAI generative AI tool offerings, only ChatGPT Edu is covered by InfoSec’s third-party security assessment (TPSA). This is the same security assessment that covers all use of Microsoft 365 across the University.
Accessing ChatGPT Edu
All current staff and students at the University of Oxford have access to ChatGPT Edu. To log in to your supported account, follow the below process:
- Go to https://chatgpt.com/
- Click the Log in button to begin the process.
- Enter your Single Sign-On (SSO) email address in the format abcd1234@ox.ac.uk and press Continue. (Please note that using a department alias such as @it.ox.ac.uk will not work).
- Choose Oxford University as your option
- You will be directed to the standard University SSO log-in process.
- You will see a few onboarding pop ups and then you can start using ChatGPT.
Verify protection - Look for "Oxford University" branding in the interface
Warning: If you don't see Oxford branding, you're in the public version - do not enter any University or otherwise confidential data. Personal AI accounts, or accounts logged into using anything other than the University’s SSO credentials, should not be used for University work or study.
Note: ChatGPT does not log you out automatically between each session. If you are using a public or shared device, you should log out after each use.
- Ensure you're using your SSO email (abcd1234@ox.ac.uk) and not your department email
- Try logging in via an incognito tab (Ctrl + Shift + N).
- Check OpenAI’s status page for outages.
- If issues persist, contact OpenAI Help Center
Access to ChatGPT Edu will end on the same day that your role or study finishes. This may differ from your University card expiry date.
Before your final day, you should copy any content you wish to retain. This includes:
- Reviewing chat history and copying relevant material
- Generating summaries of key conversations
- Creating reusable prompts to replicate important outputs
- Saving custom instructions and stored memories
If you are moving roles internally, or taking time out of your studies, access to ChatGPT Edu stops with the end of your current contract or studies. Access will resume with the start of your new role or course, but your account history may not be retained. You should therefore follow the instructions above to ensure unplanned loss of history.
Having trouble with your ChatGPT Edu account?
- Consider first seeking support from the company whose product you're using:
ChatGPT Edu: For access and activation queries, please use the OpenAI help portal. You can use the chat at the bottom of the page to ask questions and connect with support by clicking on the Message tab. If you are unable to resolve your issue through the help portal, then you should contact OpenAI support directly by email at support@OpenAI.com.
If your query is about whether an outage is affecting your connection to a particular tool, try the OpenAI Status page. - For simple queries regarding University-supported GenAI tools and support, use the AI Competency Centre chatbot to be directed to relevant information.
- For support accessing AI services, contact the Central IT Service Desk.
ChatGPT and Microsoft Copilot service statuses are now visible on the University's IT Services status page, under Communication and Collaboration ➡️ AI Tools. If you are struggling to access one of these services, please check this page for tool disruption.
Using ChatGPT Edu
Once you are logged in to ChatGPT Edu, the following guides are available to help you navigate the interface and learn how to make this tool work for you. Full details of all the features in the University of Oxford ChatGPT Edu workspace can be found further down.
We also offer the following training specifically for ChatGPT Edu:
This tab covers basic information on the structure of the ChatGPT interface.
This powerful tool offers revolutionary support for work cases spanning administration, research, education, and beyond. Its chief limitation is user imagination. It is one of the jobs of the AI and Machine Learning Competency Centre to help new and experienced users alike explore these possibilities.
Fundamentally, ChatGPT works by a call-and-response kind of conversational interface. The user sends a request or statement to the AI (called a “prompt”) and then the AI responds to that prompt in a way that resembles a text message conversation.
ChatGPT Chat Interface
The main chat interface has several major parts. The most important is labeled “Message ChatGPT”. This is where you click to type in your message and “talk” to the AI.

The other five elements are labeled below:
- Switch which “model” you want to use: Think of the *model* as the particular AI brain that you want to talk to. They range in terms of abilities and intelligence. In the image above the model GPT-5 is selected - this was ChatGPT's flagship model released in August 2025. In March 2026, OpenAI released GPT-5.3 which is the current flagship model.
- Attach files: You can upload upload directly from your machine or pull them in from OneDrive or Google Drive.
- Choose tools: ChatGPT offers a variety of tools that can enhance the conversation with the AI in interesting ways.
- Study & Learn is a feature that facilitates step-by-step learning through guided prompts, hints, and knowledge checks rather than direct answers.
- Image creation is a function that lets you ask the AI for a picture and it will create one for you.
- Web Search is a function that allows ChatGPT to search the internet for information and links.
- Canvas is a tool that lets you edit text that the AI generates. This is useful if you are drafting content like a letter where you may want the AI to edit specific parts, sentences, or words without rewriting the whole document.
- Dictate is a function that allows you to dictate your prompt rather than type it out
- Start Advanced Voice Mode: This is a mode that allows the user to speak directly to the AI and receive responses via speech. You will know that Advanced Voice Mode is activated because a blue circle will appear on the screen. The transcription of your conversation will be available in the chat after you exit out of this mode.
ChatGPT Extended Interface
Beyond the chat window, ChatGPT offers additional functionality across the platform.
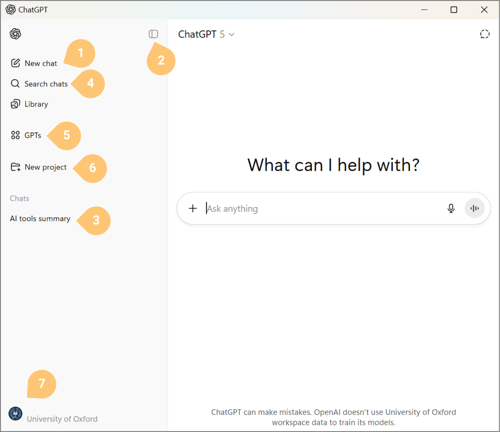
- Start New chat. This button allows you to start a new conversation from scratch.
- Hide/Open Chat History Sidebar. This button allows you to hide the entire left-hand sidebar to focus exclusively on the conversation that you are currently having with the AI.
- Chat history. This section catalogues a list of your past conversations with the AI. ChatGPT will automatically name these conversations based on the content of what you have discussed with the AI. If you wish to rename them, hover over the name and then click the three dots which will reveal options to rename and archive that conversation.
- Search chat history. This function allows you to search through all of your past conversations at once, so that you can find all the conversations that relate to a specific topic. This can be super handy if you recall having a conversation about a certain topic, but you can't find it in your chat history.
- Explore GPTs. Custom GPTs are ready-to-go conversations with the AI that are already primed with context and background information. Once you initiate one of these custom GPTs, you'll be able to hit the ground running to get useful responses from the AI that may have otherwise taken a while to elicit in a normal conversation window.
- Projects. This feature lets you organize related chats, files, and data in one workspace, keeping everything for a specific task or topic together.
- Settings. Settings contain a lot of useful features that are applicable to more advanced applications.
ChatGPT Keyboard Shortcuts
- Type / in chat to quickly choose tools
- Type @ in chat to call a recently used GPT
- Type Cmd/Ctrl + / to see a list of other keyboard shortcuts
If you are a brand new user of ChatGPT, you many find the following videos useful. These are recordings offered by OpenAI (the company behind ChatGPT) to onboard new users.
ChatGPT 101
ChatGPT 102
For new users who want to get onboarded quickly, this module on Canvas offer a step by step overview of basic concepts and prompting practices.
Putting AI to Work series
This section offers a series of videos that are focused on how to use ChatGPT in the context of work. If you want to skip over the background knowledge and jump right into an overview of how to use ChatGPT Edu in your workflow, check out these videos.
🔗 Put AI to Work: Lessons from Hundreds of Successful Deployments
Unlimited features
The following features within Oxford's ChatGPT Edu workspace are those which can be used without any usage limits - there may be some discrepancies between what is enabled for staff and what is enabled for students. The unlimited features included in ChatGPT Edu at Oxford are:
ChatGPT models:
These models are available to all staff and students.
- GPT-5.3
- GPT-5.3 Instant
- GPT 5.2 (legacy)
- GPT 5.2 Instant (legacy)
- GPT-5-mini (legacy)
- GPT-5 Thinking mini (automatically triggered by GPT-5.2 for more difficult tasks but cannot be selected by the user)
Specific tools within ChatGPT Edu:
You can select these tools in the drop down menu or by typing / in the chat but you can also trigger them by asking in the prompt (for example, "generate an image of" or "search the web for..." or "use Canvas").
- Web search
- Canvas (distinct from Oxford’s Canvas VLE)
The model powering ChatGPT Edu can also call tools that cannot be selected in the interface but can be triggered by asking in the prompt. They are:
- Memories - you can say “remember this about me” or “what do you remember about me?” or “forget this memory” - sometimes the model will choose to call the memories into its context when it think it may be relevant
- Code Interpreter - this is when the model writes and runs computer code to generate part of the answer (for instance, when you upload a spreadsheet and ask the model to analyze the data). Note: You can enable the Code Interpreter tool as a capability in custom GPTs.
Modes of interaction available to the user
- Dictate - speak about what you want included in the prompt (represented by the microphone symbol)
- Study mode (this mode changes the behaviour of the model and is equivalent to changing the prompt)
Notable ChatGPT Edu unlimited features
Apps (formerly known as Connectors) let ChatGPT securely connect to third-party applications so that you can search files, pull live data, and reference content directly in your ChatGPT chats.
For any App, individuals must still decide whether they wish to enable an App, and once enabled, it can only access files they already have permission to view.
Available Apps
Apps available to staff at the University will appear in the 'For University of Oxford' section under Apps (found in the sidebar of ChatGPT). Apps in other sections are not available for use in the Edu platform.
To enable an App, select it from the App menu and connect the relevant account.
The current Apps available to staff are:
- GitHub
How to Use Apps
Once connected, your Apps will appear in the tool selection menu (shown by the + symbol to the left hand side of the chat input box) under the 'More' tab. You can ask ChatGPT to search files, fetch live data, or reference documents by asking it to use that specific app, or by manually selecting and enabling this tool in Settings.
Remember: Apps can only access files that you have permission to access through your connected accounts.
Projects are smart workspaces that keep everything related to a long‑running effort in one place. You can group together chats, upload reference files, and add custom instructions so ChatGPT remembers what matters and stays on‑topic. With memory, context, and flexible tools, they’re ideal for repeated and evolving work such as writing, research, planning, and more.
Shared projects are not currently enabled in the University's workspace.
View a short video overview of Projects created by OpenAI.
With a SSO-linked ChatGPT Edu account, you can:
- Create and manage custom GPTs
- Share custom GPTs to the University's workspace and externally (please refer to guidance on sharing custom GPTs)
- Access custom GPTs shared in the University's workspace (this does not apply to third-party GPTs due to data concerns)
We have created an Oxford GPT Library to showcase some of the custom GPTs created and shared within the University's workspace.
Be aware that any data used to create a custom GPT may be accessed by the user of the GPT through a prompt. Therefore, any GPTs shared outside the University should not include personal or confidential information.
Most custom GPTs are used privately by their creators but they can be shared by clicking on the Share button in the GPT editing interface and then choose the appropriate option under Access.. There are three different access options:
- Invite specific users to use the GPT directly (within the Oxford ChatGPT Edu workspace)
- Create a link only users with the link can use
- Publish to the GPT Store
All of the three options can be limited to Oxford University Edu account only or they can include external users.
View a short video overview of Custom GPTs created by OpenAI.
Tips and tricks for building Custom GPTs
These next resources are focused on offering tips and tricks for building Custom GPTs which are AI Bots in ChatGPT that are tailored to execute specific tasks with a relatively high degree of reliability.
Tasks allow you to schedule actions that ChatGPT can do on your behalf (for example, summarise the week’s top news from a page, create a daily French lesson).
To schedule a task, simply ask ChatGPT in a chat that you want to do this - describe the task and the frequency. You can schedule one-time or recurring tasks. Each task runs automatically based on the schedule you define. You can view, edit, or cancel your active tasks from the Tasks page.
Tasks are currently supported on ChatGPT Web, iOS, Android, and macOS. They are not supported on the Windows Desktop app. The Schedules page, which is used to view and manage all tasks, is currently available only on ChatGPT Web.
Limited features
Some of ChatGPT’s features (5.4-Thinking, Codex, Voice Mode, Video and Image Generation) use significant shared resources. From 1 December 2025, individual, weekly usage caps were introduced for these more intensive features, to ensure fair access to them and to allow the University to consider offering further features and models such as Deep Research, GPT-5.4 Pro, and expanded provision of GPT-5.4 Thinking on an internal recharge basis, in response to demand.
Weekly limits on individual use apply to the following features:
- GPT-5.4 Thinking model
- GPT-5.2 Thinking model (legacy)
- Image generation
- Voice mode - have a live conversation (represented by the soundwaves symbol)
- Video (within voice mode on mobile app only)
Access to OpenAI’s flagship GPT-5.3 and 5.3 Instant models remains uncapped for all users, as part of the University’s inclusive provision. These models feature auto-thinking capabilities so can both be used for complex queries.
The limits on individual weekly use mean that, in addition to unlimited use of GPT-5.3 and GPT-5.3 Instant, you can initially use a maximum of one of the following in a seven-day period. These limits may be subject to change:
- 20 GPT-5.4 or GPT-5.2 Thinking messages, or
- 40 minutes of Voice Mode, or
- 40 images generated, or
- 40 Codex queries
These can be allocated flexibly; for example, you could use 10 GPT-5.4 Thinking messages and 20 minutes of Voice Mode in one week.
What happens if I expect to regularly hit my weekly limit?
In response to demand, the University is now offering the option to purchase elevated access to ChatGPT Edu.
You can request access to higher limits in ChatGPT Edu through our Payment for Higher Limits form. Please note this is paid access with differing tiers of payment. You must have sufficient funding to cover this and the approval of your budget holder. This elevated access option also covers use of GPT 5.4-Pro and Deep Research in ChatGPT Edu. Purchase can only be made through internal recharge and not by personal funds.
Get in touch
If you have any questions or feedback about usage caps for these features within ChatGPT Edu, please contact ChatGPTSupport@digital.ox.ac.uk
Notable ChatGPT Edu limited features
When should I use GPT-5.4 Thinking?
GPT‑5.3 is the default model in ChatGPT Edu and is suitable for most everyday tasks such as drafting, brainstorming, summarising, and light editing. When starting a complex piece of work, start out with GPT-5.3 and if you notice that the task requires careful planning, multiple passes, and tracking many conditions, then move the conversation into GPT-5.4 Thinking.
GPT‑5.4 Thinking is an advanced option with weekly usage limits. Here are 5 examples of where using this more powerful model may be beneficial.
- Break a complex goal into sub‑tasks (e.g. Converting messy notes into a research proposal, then iteratively refining sections)
- Keep track of many constraints at once (e.g. Planning an event or programme that must satisfy logistical, budgetary and accessibility requirements)
- Reason across multiple documents or sources (e.g. Analysing survey responses and supplementary documents together to surface patterns and implications)
- Support complex decision‑making and trade‑offs (e.g. Evaluating different options for a new service, tool or workflow and articulating pros/cons, risks and implementation steps for each)
- Designing or reviewing multi‑criteria assessments (e.g. Checking exam questions or assignments for coverage of skills, difficulty balance, and inclusivity considerations)
In short: choose GPT‑5.4 Thinking for complexity, not simply for “more accurate” answers.
See more about when to use GPT-5.4 Thinking on our Canvas resource page.
What are Thinking models and which ones are available in ChatGPT
- Thinking models make a list of steps before you the answer (this may include doing a search or a calculation) and they take longer - they produce better results
- You can encounter two Thinking models in ChatGPT
- GPT-5 Thinking Mini - this is triggered automatically by GPT-5.3 Flagship or when you ask the Flagship model to "think harder". This is a less powerful model than GPT-5.4 Thinking but it is faster and does not count towards your usage limits.
- GPT-5.4 Thinking is more powerful than GPT-5 Thinking Mini but it takes longer and does count against usage limits. To use it, you have to select in the model selector at the top of the page. Note: You may have to manually switch to GPT-5.3 (Flagship) in a new chat after using GPT-5.4 Thinking.
Codex is a coding agent using GPT models that can be accessed via the ChatGPT Edu login but is not part of ChatGPT itself.
Please note: Codex is currently only available for University staff members.
The different Codex models are:
- GPT-5.3- and 5.2-Codex
- GPT-5.1-Codex-max
- GPT-5.1-Codex-mini
GPT-5.3- and 5.2-Codex and GPT-5.1-Codex-max can be used for local tasks, cloud tasks and code review, GPT-5.1-Codex-mini can only be used for local tasks.
Codex covers several different capabilities and the ones currently enabled are as below:
- Codex Cloud / Web Codex Cloud is accessible at https://chatgpt.com/codex or by clicking the Codex button in the left sidebar when on https://chatgpt.com. Using Codex Cloud, users can connect to a GitHub repository, and ask in natural language to make changes. Codex Cloud will not make changes directly to the codebase but let the users create create pull requests with suggested changes in the associated GitHub repository.
- Codex App The Codex app is a standalone desktop application for coordinating AI coding agents (currently only available on macOS). It enables parallel workflows, multi-agent orchestration, project management features (including worktrees and Git support), and long-running tasks across projects.
- Codex CLI This is a coding agent that software engineers can access through the terminal using a command line interface. Users can download the tool from the link, and login using their ChatGPT Edu account. This still uses natural language interactions to allow users to make changes to code. Unlike the Codex Cloud, you do not have to explicitly connect to a GitHub repository. This tool has access to your local files, and can run commands directly on your computer.
- Codex IDE This is similar to Codex CLI except that this is an extension directly for an IDE program. Currently OpenAI offer Codex IDE extensions for three popular IDEs, Visual Studio Code, Cursor, and Windsurf.

